
Understanding OS transfer methods proves crucial for efficient system management. Cloning creates an exact replica of your drive, preserving all data and settings. Migrating, however, involves transferring essential files and applications to a new system. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges. Recognizing the difference between disk clone and OS migration helps in choosing the right approach for your needs. Whether upgrading hardware or ensuring data safety, selecting the appropriate method impacts performance and reliability. Explore these key differences to make informed decisions and optimize your OS transfer process.
Key Takeways:
The following table provides a clear, side-by-side comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of Disk Cloning and OS Migration to help you understand their core differences.
| Feature | Disk Clone | OS Migration |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages (Pros) | • Creates a perfect, bootable 1:1 replica of the entire source disk, including the OS, applications, files, and even deleted data. • Excellent for full backup and disaster recovery. If the original drive fails, the cloned drive can be swapped in to get the system running immediately. • Simpler process conceptually; the goal is to make an exact copy without selective filtering. | • Selective and Intelligent: Primarily focuses on moving only the necessary operating system files, boot files, and installed applications to a new drive. • Saves time and storage space as it does not copy unnecessary user data or empty sectors. • Ideal for upgrading to a smaller SSD as it only transfers system-related data, bypassing the capacity limitation of cloning. |
| Disadvantages (Cons) | • Less flexible. Requires the target drive to be equal to or larger than the used space on the source drive. • Time-consuming, especially for large drives, as it copies every sector (including empty ones). • Can transfer clutter. Copies all user files and potentially redundant data, which may not be desired for a clean system upgrade. | • Not a full backup solution. It does not create a complete sector-by-sector image of your drive for disaster recovery. • Higher risk of application or boot issues if the migration process does not correctly identify and transfer all necessary system dependencies. • May require manual backup of user data before proceeding, as it typically leaves files behind on the original drive. |
In summary: Choose Disk Clone for a full, reliable backup and recovery solution. Choose OS Migration for a more efficient system upgrade, especially when moving to a smaller drive or when you want to keep your data separate.
Definitions and Explanations of Clone and Migration
What is Disk Clone?
Disk clone involves creating an exact replica of a hard drive. This process copies every bit of data from the source disk to a target disk. The primary purpose of disk clone is to preserve all system files, applications, and settings. Users often choose cloning for complete system backups or hardware upgrades like cloning ssd to a larger ssd. Cloning ensures that the new drive functions identically to the original.
Users frequently employ disk cloning in several scenarios:
- System Upgrades: Cloning facilitates seamless transitions to larger or faster drives.
- Data Backup: Cloning provides a reliable method for creating full-system backups.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloning allows quick restoration of systems after failures.
What is OS Migration?
OS migration involves transferring essential files and applications to a new system. Unlike cloning, migration does not create an exact copy of the original drive. Migration focuses on moving user data and applications while leaving behind unnecessary files. This method suits users who wish to start fresh on a new system.
OS migration proves beneficial in various situations:
- New System Setup: Migration helps set up new systems without duplicating old clutter.
- Data Transfer: Migration efficiently moves user data between different operating systems.
- Registry Optimization: Migration reduces registry bloat by omitting outdated programs.
How to perform a Disk Clone and OS Migration freely

Is there a tool that allows users to perform system cloning and migration? As a free disk cloning and migration software, WittyTool DiskClone is the solution you’re looking for.
It offers a user-friendly interface and powerful features. It ensures fast and secure cloning and migrating for Windows users. For example, perform a network clone disk. Meanwhile, it is the world’s first software to support recreating recovery partitions if your recovery partition was missing!
Download the software and follow this guide to easily complete these complex tasks step by step.
How to Clone an OS via this disk cloning software?
Step 1: Choose Disk Clone Mode
Click on the left panel to access the clone page, then select the disk clone mode.
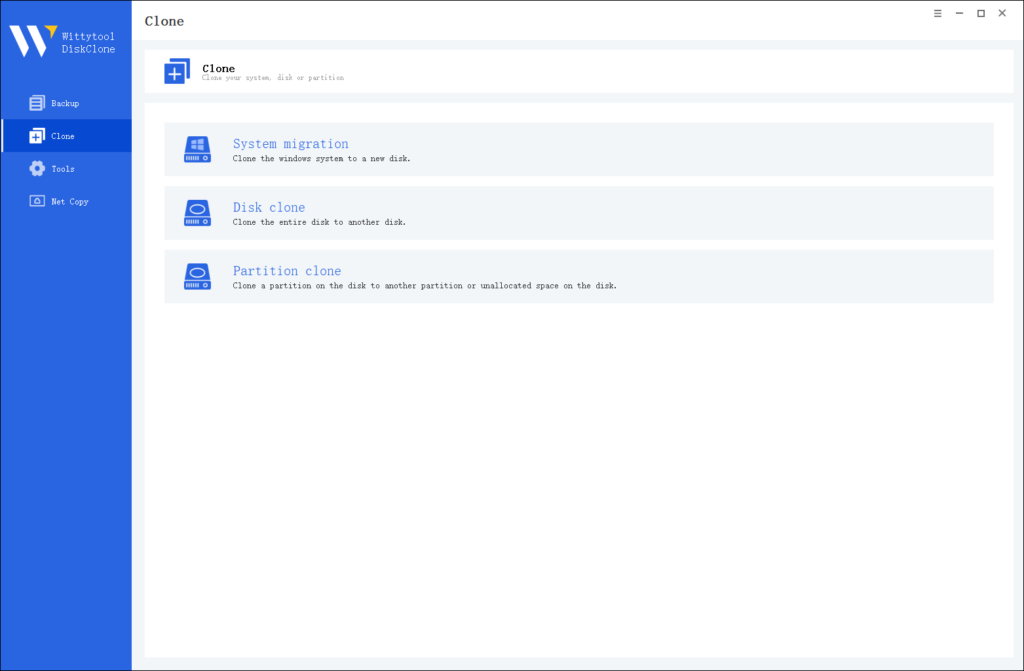
Step 2: Choose Source Disk
Pick the disk from the list view. The layout of the selected disk will be displayed at the top of the list view.
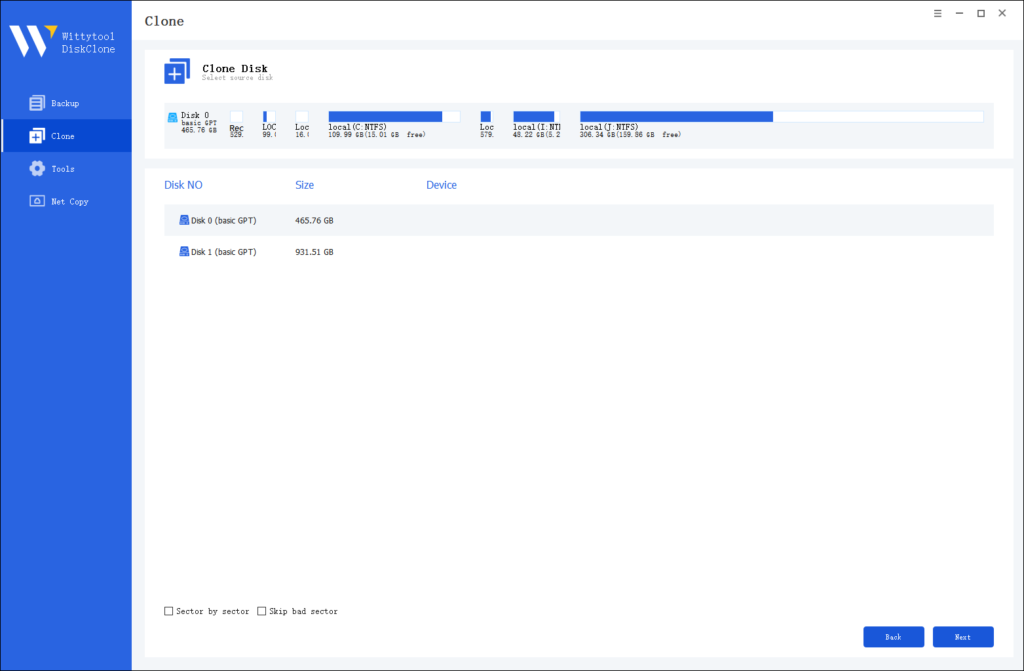
Note:
*Sector by Sector: This option should be selected if the source disk has bad sectors or if the file system on the disk is damaged. It ensures that all sectors on the source disk are cloned.
*Skip Bad Sectors: If the source disk has bad sectors, select this option. Wittytool DiskClone will ignore the bad sectors and clone only the undamaged ones. This method is suitable for older disks that may have bad sectors.
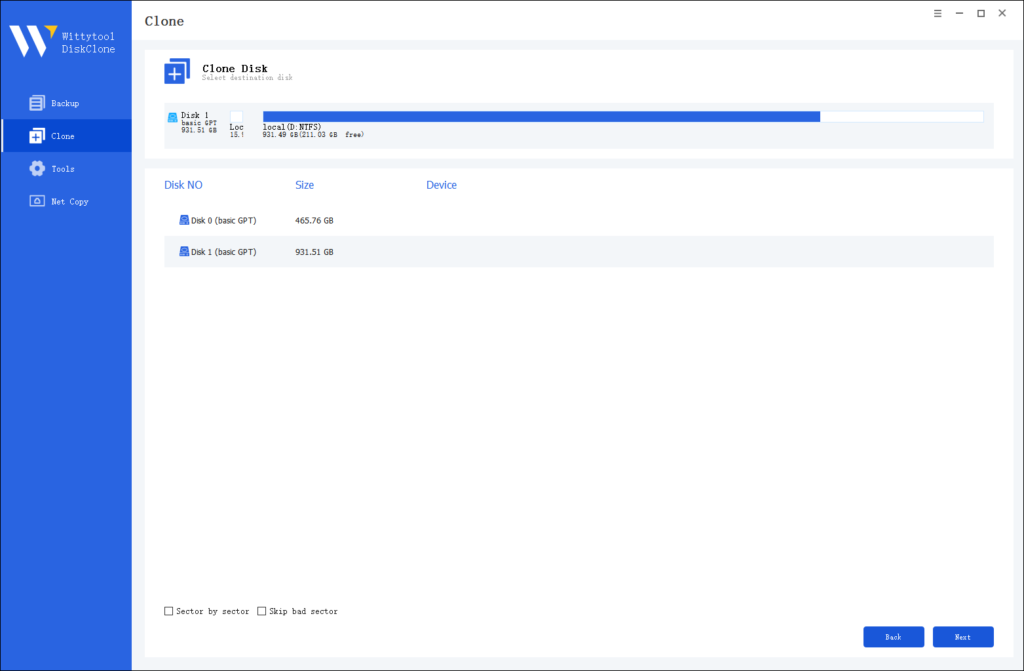
Step 3: Choose Destination Disk
Select the target disk.
Step 4: Resize Partition and Start Cloning
You can resize the partition on the target disk if needed. Click the “Start Clone” button to begin the cloning process.

How to Migrate an OS via this OS Migration Software?
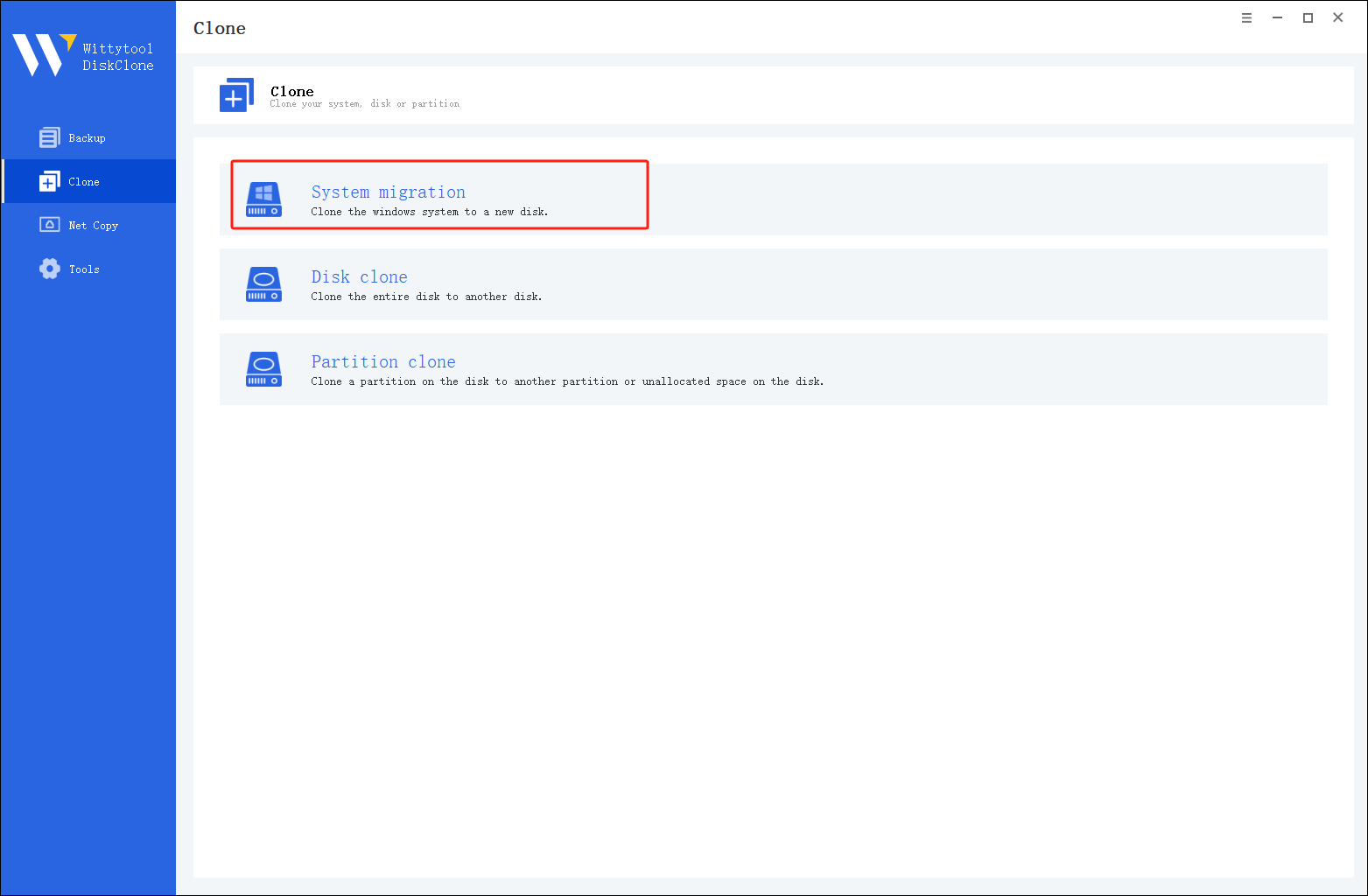
Step 1: Select System Migration Mode
Access the clone page by clicking the left panel, then choose the System migration mode.
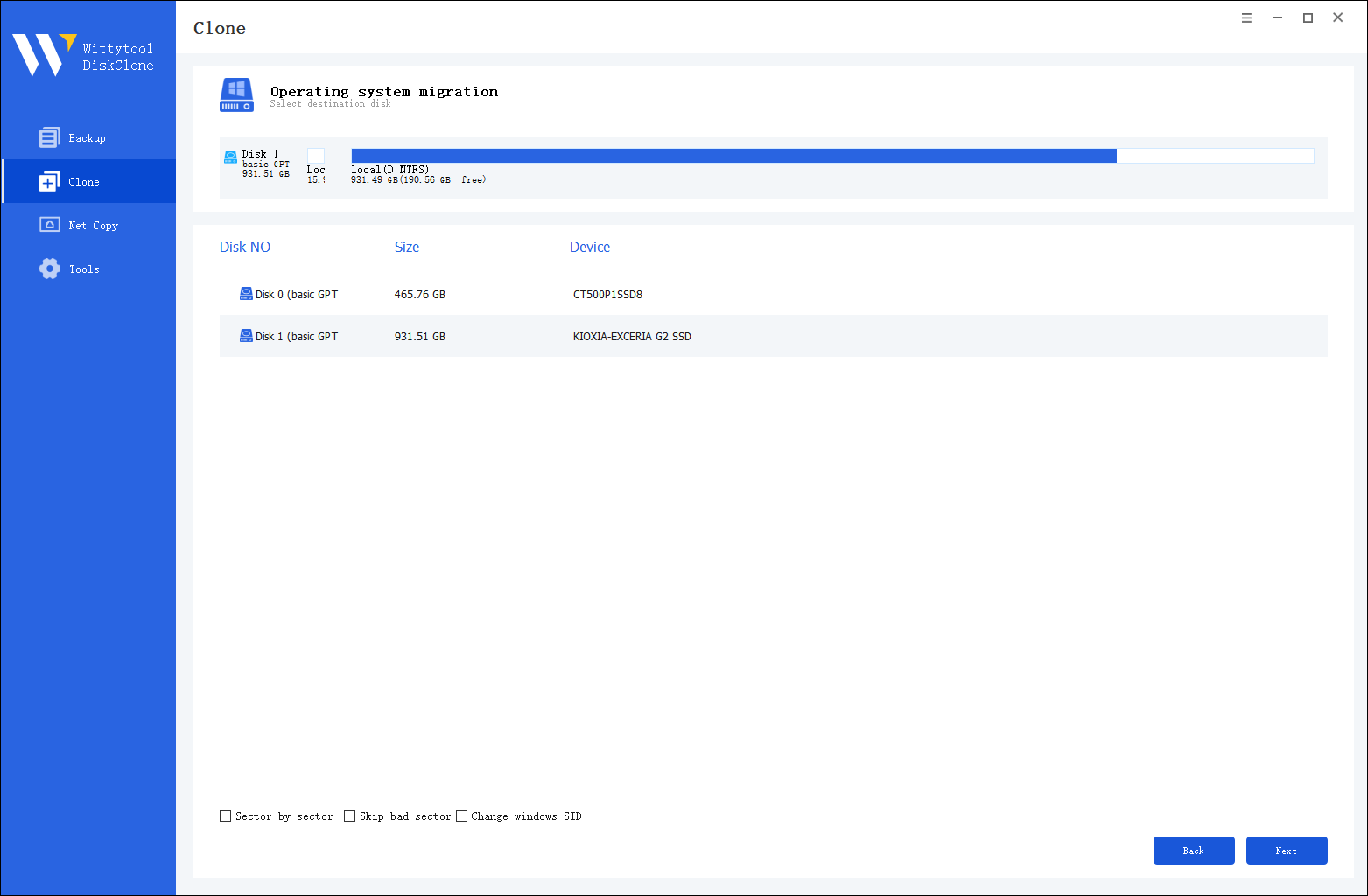
Step 2: Select Destination Disk
Choose the destination disk from the list. The layout of the selected disk will appear at the top of the list.
Note:
*Sector by Sector: Select this option if the source disk has bad sectors or a damaged file system. This ensures all sectors of the source disk are cloned.
*Skip Bad Sectors: If the source disk contains bad sectors, choose this option. Wittytool DiskClone will bypass the damaged sectors and clone only the intact ones, making it ideal for older disks with bad sectors.
*Change Windows SID: When cloning multiple machines on the same network, select “Change Windows SID” to prevent security issues related to network access.
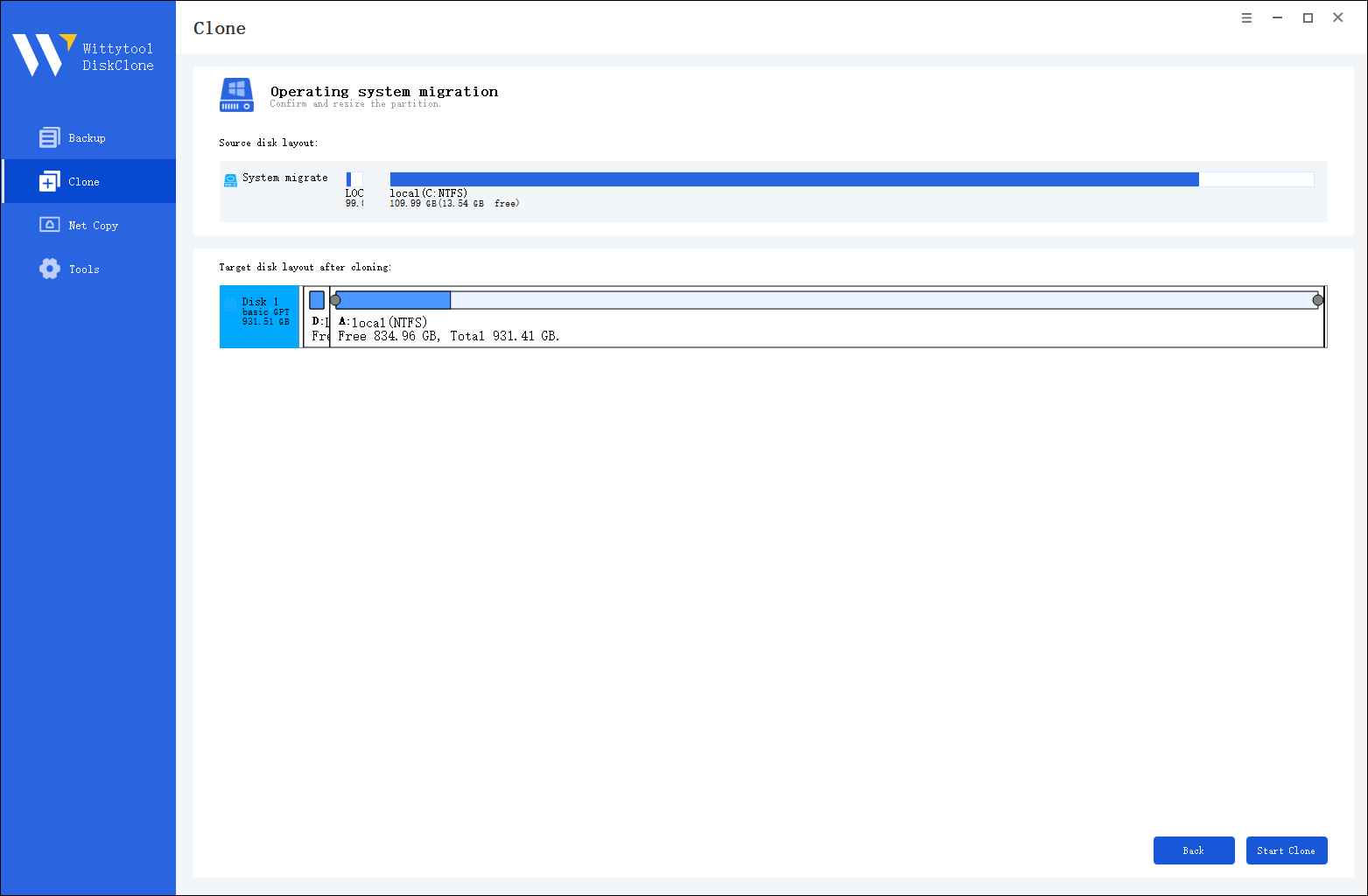
Step 3: Confirm Partition Size
Review and resize the partitions on the target disk as needed. Once ready, click the “Start Clone” button to begin the cloning process. After cloning is complete, set the target disk as the boot disk in the BIOS and boot the system from it.
Pros and Cons Between Clone and System Migration
Advantages of Disk Clone
Disk clone is fast and efficient, allowing you to quickly create an exact replica of your drive. It’s ideal for upgrades, minimizing downtime by enabling immediate replacement of failed drives. Cloning ensures data integrity, preserving system files, applications, and settings, making it a reliable safeguard against data loss.
Also read: How to Clone Your Disk and Change Windows SID
Disadvantages of Disk Clone
Disk clone requires substantial storage, as the target disk must be equal to or larger than the source. This can be challenging for users with limited space, necessitating careful planning. Compatibility issues may also arise due to differing hardware configurations, so it’s important to verify that the new drive supports the cloned data to avoid potential problems.
Advantages of OS Migration
OS migration offers flexibility by allowing users to transfer only essential files and applications, leaving behind unnecessary data. It’s ideal for those wanting a fresh start. With extensive customization options, users can optimize the system registry, reduce bloat, and enhance performance. Migration also enables smooth transfers between different operating systems, resulting in tailored system setups.
Disadvantages of OS Migration
OS migration is a complex process requiring careful attention to detail at each step, especially when transferring files between different operating systems. Compatibility challenges often arise, making it difficult for users without technical expertise.
There is also a risk of errors during migration, which can result in incomplete transfers or data loss. The chance of mistakes increases with large data volumes, so post-migration checks are essential to ensure everything functions correctly. Errors can disrupt workflows, but proper planning and execution can minimize these risks.
Choosing Between Disk Clone and OS Migration
When to Choose Clone
Cloning suits scenarios requiring exact replicas. Users upgrading to larger drives benefit from cloning’s speed and efficiency. Cloning ensures complete data integrity, preserving system files and settings. This method proves ideal for disaster recovery and full-system backups.
When to Choose Migration
Migration fits situations where customization is key. Users setting up new systems without old clutter find migration beneficial. Migration allows selective transfer of essential files and applications. This method enhances performance by reducing registry bloat. Users seeking a fresh start often prefer migration.
Case Studies:
- Accenture Cloud Migration Journey: Successful migration requires careful planning. Accenture completed migrations on time and budget by addressing complexities.
- Thomson Reuters Migration Challenges: Collaboration is vital. Thomson Reuters realized the need for business and application teams to take ownership.
- Cloud Migration Strategies: Spotify and Betabrand highlight the importance of preparation. Advance planning led to successful cloud migrations.
Choosing between clone and migration depends on specific needs. Consider hardware compatibility and time constraints. Evaluate scenarios to select the most suitable method.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between disk clone and os migrating OS helps you make informed decisions. Cloning creates an exact replica of your system, while migration transfers essential files to a new environment. Your choice depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like hardware compatibility and time constraints. Evaluate practical steps for each method. Ensure data backup and post-implementation checks for success. Choose the right approach to optimize your system’s performance and reliability.
FAQ
What is a benefit of cloning a hard drive versus installing from installation media?
The primary benefit is immense time savings and convenience. Cloning transfers your entire existing system—including the operating system, all your installed applications, personal files, settings, and preferences—in one operation. After cloning, your new drive will be an exact replica of the old one, and you can resume work immediately. In contrast, installing from media requires a fresh OS installation, followed by reinstalling every single application, reconfiguring all your settings, and restoring your personal files from a backup, which can take hours or even days.
Is it better to clone to move your OS, or do a fresh install?
This depends on your goal:
- Choose Cloning if your priority is speed, convenience, and preserving your current workflow. It’s the best choice for directly upgrading your hard drive or quickly replacing a failing drive without any disruption.
- Choose a Fresh Install if your priority is system cleanliness and performance. A fresh install eliminates system clutter, residual files from old programs, and potential software conflicts that may have accumulated over time. It results in a clean, fast, and stable system, but requires significant time and effort to set up again.
In short: Clone for efficiency, Fresh Install for a pristine system.
DiskGenius system migration vs clone disk?
In DiskGenius, these two functions serve different purposes, aligning with the general definitions provided earlier:
“System Migration” (or “Migrate OS”) function is more intelligent and selective. It is designed specifically to move only the system-related partitions (OS, boot files, and installed applications) to a new drive, typically an SSD. Its key advantage is that it allows you to migrate your system to a smaller drive (as long as it has enough space for the system data), which the “Clone Disk” function cannot do if the source drive’s used capacity exceeds the target drive’s size.
“Clone Disk” function creates a sector-by-sector identical copy of the entire source disk to the target disk. This includes all partitions, data, and unused space. It is ideal for creating a full backup or replacing a drive with one of equal or larger capacity. It’s worth noting that while DiskGenius is a powerful option, users often explore a capable diskgenius free alternative for these tasks to meet different needs or budget constraints.

